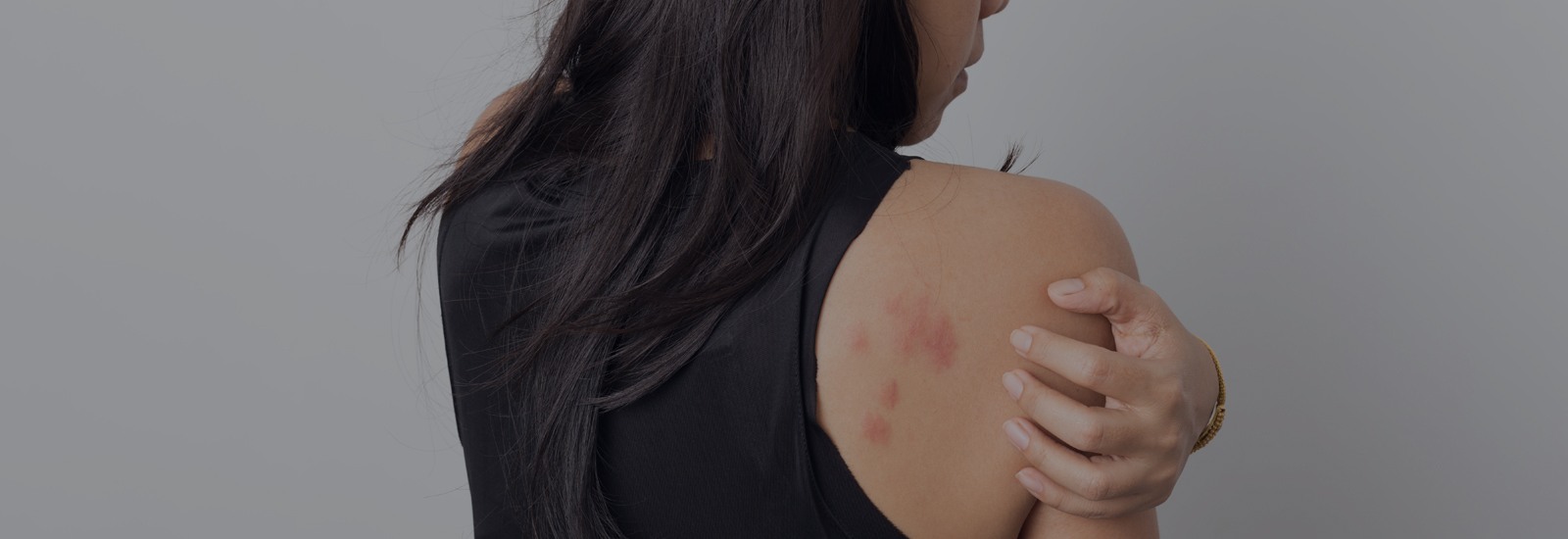
Do you ever get bumps that itch like bug bites but aren’t really bug bites? Well, that may be a case of Urticaria.
Urticaria, also known as hives, are swollen red or skin-coloured bumps on your skin that may appear and disappear quickly, and the itching can range anywhere from mild to severe. In some cases, they can also burn or sting and what’s more? They can appear anywhere on the body, including hands, face, lips, ears, throat or tongue. Hives affect around 20% of people at some point in their lives.
Urticaria, that also goes by different names such as welts, wheals or nettle rash are not contagious. However, they can sometimes last for days, months or even years!

What are the different types of Urticaria?
There are many different types of Urticaria. They can either be acute or chronic.
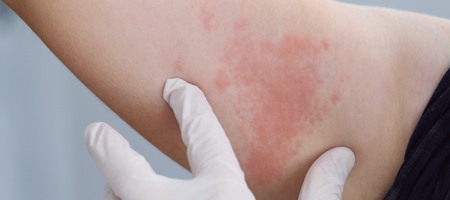
Acute
Urticaria:
The most common type of hives, Acute
Urticaria symptoms last less than six weeks and can be caused by
insect bites, medications, infections, some internal disease or
consuming foods like nuts, chocolates, fish, tomatoes, eggs,
berries or milk. Even drugs like aspirin, ibuprofen or certain
painkillers can cause Acute Urticaria. They usually affect the
face, toes, fingers, neck and sometimes even men’s
genitals!
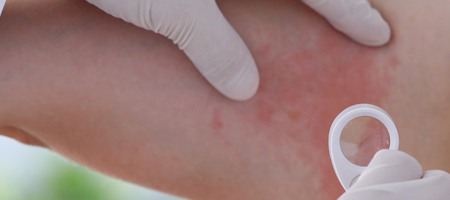
Chronic
Urticaria:
Chronic Urticaria will last more than
six weeks. The cause of Chronic Urticaria is difficult to
identify and oftentimes, impossible. However, in some cases,
Chronic Urticaria causes can be linked to the immune system or
to diseases like thyroid, hepatitis or even cancer. Chronic
hives can affect a person as they can be uncomfortable and
embarrassing and can also interfere with a person’s sleep
and day-to-day life.
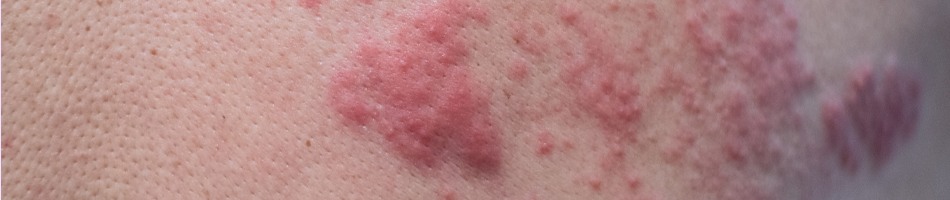
Physical
Urticaria:
In Physical Urticaria, the hives on skin happen due to a
physical reason. There are various physical hives causes
–
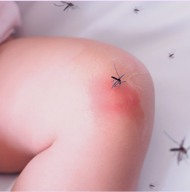
PAPULAR URTICARIA
Papular Urticaria is an allergic reaction to bites from insects like mosquitoes, fleas, mites, carpet beetles or bed bugs. Papular Urticaria in children of 2- 10 years of age is quite common.

COLD URTICARIA
Cold Urticaria can occur when your body is exposed to cold. It can appear within minutes of exposure to cold temperature and the symptoms of this type of Urticaria vary from person to person between mild to severe and sometimes even life-threatening. outbreaks.

CHOLINERGIC URTICARIA
This type of Urticaria is an allergic reaction caused by increase in body temperature caused by several reasons such as anxiety, hot showers, sweating, etc. outbreaks.

SOLAR URTICARIA
Exposure to sun can cause solar Urticaria in some people. Symptoms of solar Urticaria can appear within minutes of sun exposure. outbreaks.

DERMATOGRAPHIC URTICARIA
Dermatographism is a common form of Physical Urticaria caused by rubbing or scratching the skin. Symptoms of this type of Urticaria usually start showing within minutes and generally last less than an hour.
What are the causes of Urticaria?
Urticaria is caused when the body reacts to a certain allergen and in reaction releases histamines and other chemicals. These chemicals and histamines cause inflammation and lead to accumulation of fluid under the skin, causing hives.
Some of these things are known to trigger an allergic reaction causing hives:
- Foods like peanuts, eggs, shellfish, strawberries, nuts, wheat products and some food additives
- Medications including antibiotics, aspirin and ibuprofen
- Insect bites and stings
- Latex
- Pollen
- Viral infections like common cold, hepatitis, etc.
- Physical stimulation of skin like pressure, heat, cold, sun exposure and exercise
- Blood transfusions
- Pet dander
- Dust mites
- Some plants including nettles, poison ivy, etc.
- Chronic illnesses like thyroid or lupus
- Scratching or rubbing
How do you know if it is hives or angioedema?
The biggest difference between angioedema and hives is that angioedema is the swelling of tissues beneath the surface of the skin whereas hives are bumps on the surface of the skin and can be caused by allergic reactions, medications, etc.
You know its angioedema when you notice the following symptoms -
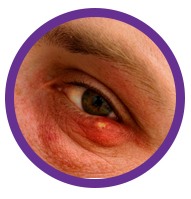
SWELLING IN THE EYES OR MOUTH

DIFFICULTY IN BREATHING AND STOMACH CRAMPS
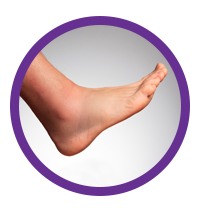
SWELLING OF HANDS, FEET OR THROAT
How is Urticaria diagnosed?
Urticaria is diagnosed depending on its type.
A single episode of hives does not usually call for extensive testing. If a food
allergy is suspected, consider keeping track of what you eat. This will help you
discover whether there is a link between what you’re eating and when you
break out with hives.
Chronic hives should be evaluated by an allergist, who will ask about your and your family’s medical history, substances to which you are exposed at home and at work, exposure to pets or other animals and any medications you’ve taken recently. If you have been keeping a food diary, show it to your allergist.
How is Urticaria treated?
Urticaria is usually treated by a dermatologist/allergist with a type of medicine called antihistamines.
Doctors and Global guidelines strongly suggest use of non sedating Antihistamines which are quite safe. It is, however, best to visit a dermatologist/ allergist to understand your condition and get treated accordingly.
When to seek emergency medical help?
If you notice hives on face or swelling in your tongue or lips or face difficulty in breathing, it can be an early symptom of anaphylaxis, a potentially fatal allergic reaction that can cause problems in breathing and send your body into shock.
You must also contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms -

DIZZINESS

TIGHTNESS IN CHEST

WHEEZING
Frequently asked questions:
Identifying Urticaria causes might be difficult and sometimes next to impossible, especially when your hives are chronic. However, if you suspect a food allergy, you might consider keeping a food journal to identify which foods are causing it. Moreover, some things are known to trigger an Urticarial rash including foods like eggs, peanuts, shellfish, etc., insect bites, antibiotics, latex, some plants, pollen, dust mites, bacterial or viral infections, physical stimuli, etc.
