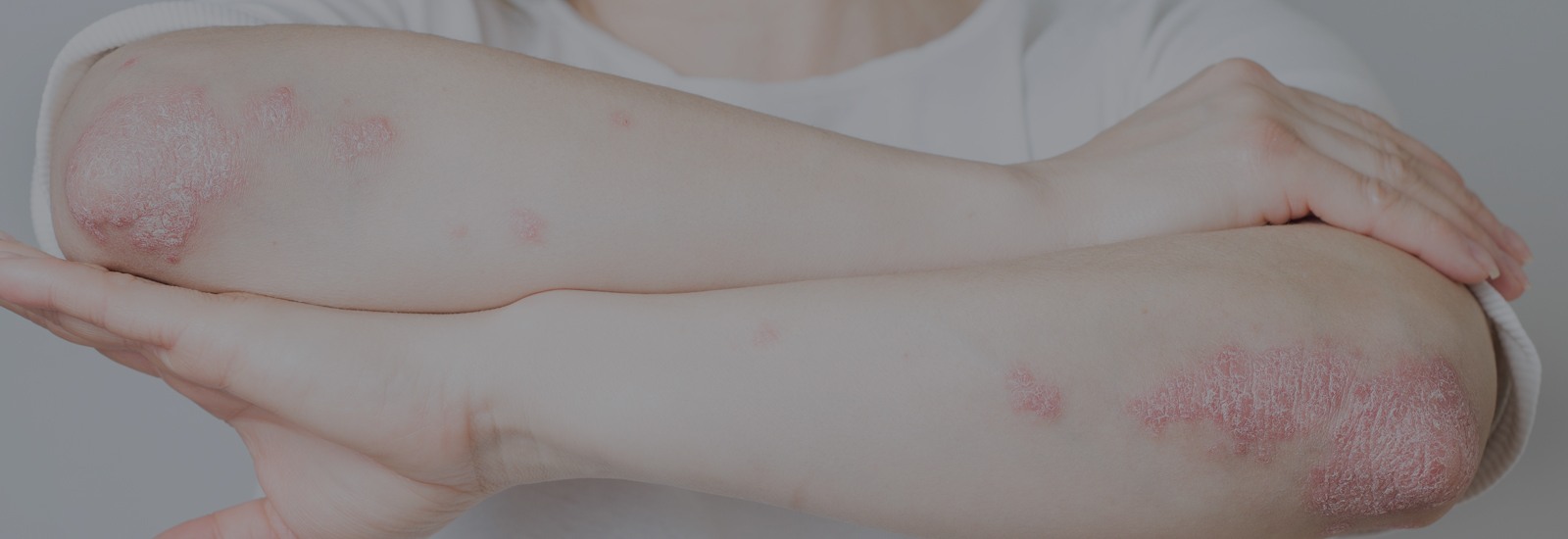
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis can be best defined as a chronic autoimmune condition. It leads to the quick build-up of skin cells. Due to this build-up, the skin’s surface looks scaly. Redness and inflammation around the scales is likely to happen next. These red patches often crack and bleed. Normally, skin cells grow deep within the layers of the skin. The skin cells then rise to the surface and later fall off. However, in people with Psoriasis, the production process of skin cells is rapid. Due to this, skin cells are unable to fall off. This overproduction causes build-up of skin cells.
Scales usually develop on joints of the body like knees and elbows. The developing of these scales can also happen on other body parts like scalp, hands, feet, neck and face.
What is the difference between Eczema and Psoriasis?
Because their symptoms are so similar, sometimes it is difficult to differentiate between Eczema and Psoriasis. This is when a biopsy can come in handy. However, not many know that Eczema and Psoriasis often respond to similar treatments. While certain types of Eczema are curable, the same cannot be said for Psoriasis.
What are the common causes of Psoriasis?
Healthcare professionals are still unclear as to what causes Psoriasis. However,
decades of research points to two main factors: Immune system and
genetics. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. Autoimmune conditions
are when the body attacks itself. In a typical human body, white blood cells
destroy invading bacteria and infections. In people with Psoriasis, this
mistaken attack leads to overproduction of skin cells.
On the other hand, genetics play an important role when it comes to Psoriasis.
Some individuals inherit genes that make them more likely to develop this
condition. If you have an immediate family member who suffers from Psoriasis,
your risk of getting it is higher.

What are the symptoms of Psoriasis?

Psoriasis usually results in scaly, reddish-white patches of skin on different body parts. Infants tend to suffer from these lesions on their neck, elbows, face, diaper area, knees and scalp. Unlike adulthood Psoriasis, Psoriasis in infants may disappear and never recur.

The most common symptoms of Psoriasis in children include
- Cracked and dry skin that bleeds
- Thick nails or fingernails that develop deep ridges
- Red areas in folds of the skin
- Soreness and itching around the affected areas of the skin

Several types of Psoriasis occur in cycles. They flare up for a few weeks and then subside for some time. Some common symptoms include
- Red patches of skin covered in silvery, thick scales
- Stiff and swollen joints
- Cracked and dry skin that itches or bleeds
- Ridged and thickened nails
How is Psoriasis diagnosed?
In addition to asking questions about your health, your health care expert will examine your scalp, skin and nails. Your doctor may even take a tiny sample of your skin to examine under a microscope. This biopsy will not only determine the type of Psoriasis, but will also rule out other skin disorders.
What commonly triggers Psoriasis?
While those suffering from Psoriasis might have different triggers, here are a few common external triggers that Psoriasis patients need to watch out for.

Alcohol
Excessive use of alcohol can cause Psoriasis to flare up. Heavy drinking is associated with more frequent outbreaks.

Stress
If your stress levels are higher than the normal range, you may experience more Psoriasis flare-ups.
Infection
When you’re sick, your immune system automatically goes into overdrive. Because Psoriasis is caused by the attack of the immune system on healthy cells, infections are known to be a common trigger.
Injury
A scrape, an accident or a simple cut may cause a Psoriasis flare-up. Additionally, vaccines, shots or even a sunburn may trigger a new outbreak.
How is Psoriasis treated?
Across the globe, currently available medicines do not offer a cure to Psoriasis. However, there are various remedies/medications which can be used to control and manage the symptoms of Psoriasis.
Prevent dry skin
Keep the air moist in your surroundings by using a humidifier. You can even use moisturizers to keep your skin soft and supple.

Eat healthy
Try to reduce your intake of red meat, refined sugars and carbohydrates. Nuts, seeds and omega-3 fatty acids have the ability to manage Psoriasis symptoms.

Stay away from fragrances
Most perfumes and soaps have chemicals and dyes that are harmful for skin. Avoid such products to prevent flare-ups.

Consume dietary supplements
Aloe Vera, vitamin D and fish oil help with mild symptoms of Psoriasis.
However, it is best to check with your health care professional before you
take any supplements.
What are the different types of Psoriasis?
Listed below are the 5 different types of Psoriasis.
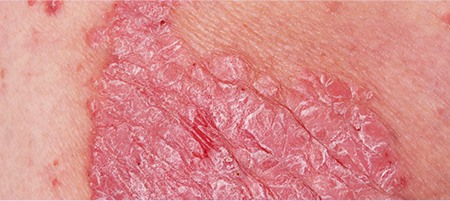
Pustular Psoriasis:
This type affects about 3 percent of people living with
Psoriasis. Its symptoms include pus-filled bumps surrounded by
reddened skin.
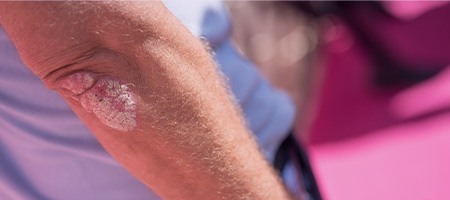
Inverse Psoriasis:
This type affects one quarter of people who have Psoriasis.
Signs of Inverse Psoriasis include inflamed skin that is smooth
and not scaly.
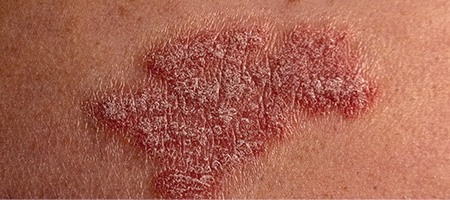
Guttate Psoriasis:
This type affects roughly 8 percent of people living with
Psoriasis. Its symptoms include small red spots caused by
inflammation.
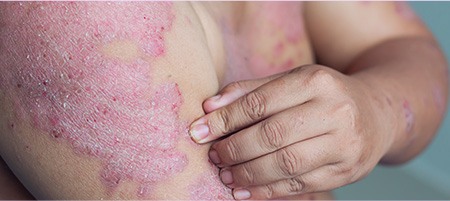
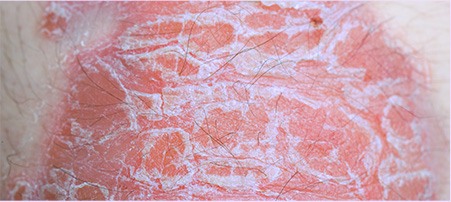
Plaque Psoriasis:
This is the most common type, affecting about 80 percent of
people living with Psoriasis. Plaques can make an appearance on
any part of the body as patches of inflamed skin with
scales.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis:
This type of Psoriasis is rare, affecting only 2 percent of
people having Psoriasis. It causes extreme redness along with
shedding of skin layers in large sheets.
FAQs of Psoriasis
External conditions like injury, infections and cold weather are the common causes of Psoriasis.