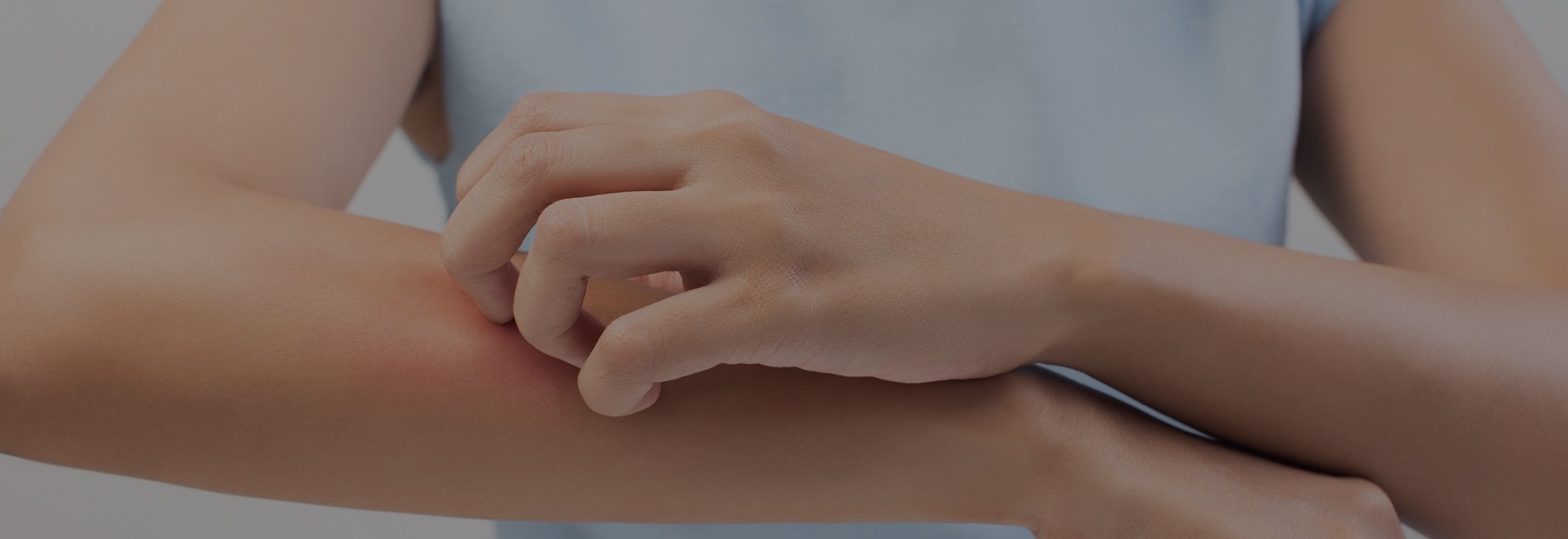
What is Eczema?
Several conditions can make your skin red, itchy and inflamed. Eczema is a term that is commonly used to describe these skin conditions. Some types of Eczema can also lead to blisters. Even though one can get Eczema at any age, it is most common in children. While Eczema as a condition has several types, the most common type is Atopic Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis. The term atopic signifies a group of conditions that have to do with the immune system. This includes asthma, Atopic Dermatitis and hay fever. Some individuals outgrow Eczema as they grow older. However, some others continue to have it well into adulthood. Eczema treatment involves no particular cure, but its symptoms can be managed by avoiding irritants. Eczema is not contagious, which means, you cannot spread it to other people. Certain types of foods such as dairy and nuts are known to trigger symptoms of Eczema. Smoke, soaps, pollen and fragrances are a few environmental triggers of Eczema.
How to differentiate between Eczema and Atopic Eczema?
Eczema is not a skin condition in itself. It causes Atopic Dermatitis. Eczema refers to a group of skin conditions that can lead to inflammation and irritation. On the other hand, Atopic Dermatitis is a common chronic skin condition that causes inflamed, red, itchy and dry skin.
What are the common causes of Eczema?
It is difficult to pin-point what exactly causes Eczema, but several health experts believe that it is caused due to a mix of environmental and genetic factors.
When it comes to the genetic factor, children are likely to develop Eczema if a parent suffers from it. The risks run even higher if both parents have an atopic condition.
When it comes to the environmental factors, here are a few -


Pets, mold, dust mites and pollen.

Eggs, dairy products, seeds, nuts, wheat and soy products.

Low and high humidity, extreme hot and cold weather, and perspiration.
Women are likely to experience a flare-up in their Eczema symptoms due to changing levels of their hormones. This usually happens during pregnancy and at certain points in the menstrual cycle.

Soaps, shampoos, disinfectants, detergents, juices from fresh fruits, vegetables and meat.

Bacteria such as viruses, certain fungi and staphylococcus aureus.

While stress is not a direct cause of Eczema, it tends to make its symptoms worse
What are the common symptoms of Eczema?
Did you know that the symptoms of Eczema vary depending on the age of the person? Most often, Eczema makes an appearance before the tender age of five and continues well into puberty and adolescence. No two people suffering from Eczema have the same symptoms.

If your child is under the age of two, here are a few common symptoms of Eczema you can look out for
- Rashes that become a bubble and then leak fluid
- Rashes that appear on the cheeks and the scalp
- Rashes that led to intense itchiness, which interferes with your child’s sleep

If your child is over the age of two, here are a few common symptoms of Eczema you can look out for
- Rashes that appear on the wrist, neck and ankles and also in the crease between the buttocks and the legs
- Rashes that tend to become lighter or darker
- Rashes that are seen behind the creases of knees or elbows
- Rashes with bumps
- Skin thickening which can then become a constant itch

Here are a few common symptoms of Eczema that adults can look out for
- Rashes that appear at the nape of the neck
- Rashes that constantly itch
- Scaly rashes
- Rashes that spread over majority of the body
- Skin infections
How is Eczema diagnosed?
Lab tests aren’t necessary to diagnose Eczema. Health practitioners most likely identify Eczema by examining the patient’s skin and reviewing their medical history. They may also make use of a method called patch testing or conduct other tests to make sure the patient isn’t suffering from any other skin disease.
How is Eczema treated?
Across the globe, currently available medicines do not offer a cure to Eczema. However, there are various remedies/medications which can be used to control and manage the symptoms of Eczema.
Eczema treatment plans are usually based on a patient’s age, symptoms and current health conditions. For some people, the condition goes away with time and Eczema treatment isn’t necessary. Unfortunately, for some others it may last lifelong.
Here are a few home care Eczema treatment options -
 Moisturizing
daily
Moisturizing
daily
 Taking
lukewarm baths
Taking
lukewarm baths
 Wearing
soft fabrics
Wearing
soft fabrics
 Using
a mild soap
Using
a mild soap
 Using
a humidifier in cold weather
Using
a humidifier in cold weather
Antibiotics prescribed by doctors can also help with Eczema treatment. Phototherapy, which involves exposure to UVA or UVB waves, can also help with Eczema treatment.
Patients need to bear in mind that even after an area of skin has healed, it is important to keep looking after it as it is likely to get irritated again.
What are the different types of Eczema?
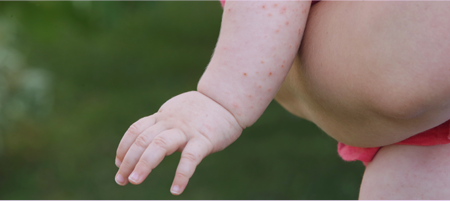
Atopic Eczema:
Atopic Eczema usually gets detected in childhood, and often goes
away by the time the patient enters adulthood. Atopic Eczema
occurs when your skin's natural barriers are weakened.

Allergic Contact Dermatitis:
This is an immune system reaction to an irritant like metal or
latex. Other common causes of allergic contact dermatitis are
bleach, jewellery, paint and soaps.

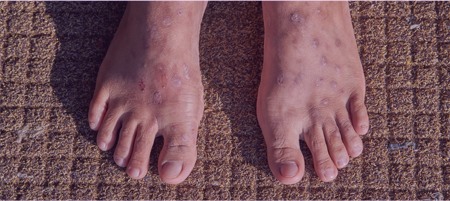
Dyshidrotic Eczema:
This type causes hey blisters to form on your feet and hands.
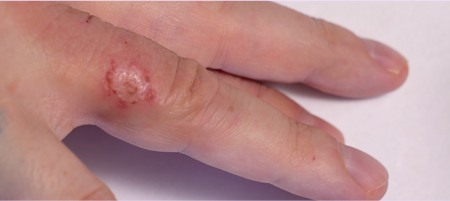
Discoid Eczema:
This type of Eczema is also known as nummular Eczema. It appears
as circular patches of inflamed skin that can be scaly, itchy
and crusted.
Stasis Dermatitis:
This type refers to skin irritation of the lower legs. Stasis
dermatitis is commonly caused because of circulatory problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Genetics and environmental factors are the main cause of Eczema.
No, Eczema is not contagious.
The most common type of Eczema is Atopic Dermatitis. It is caused by an overactive immune system.
Avoiding scratching, taking a bleach bath and moisturizing skin daily are a few ways in which you can curb the spread of Eczema.
Irritants such as wool, soaps, detergents, low humidity and emotional stress trigger Eczema in adults.